How Many Watts Is 200 Amps?
How Many Watts Is 200 Amps? An Easy Guide to Calculating Power Factor
Are you curious about “how many watts is 200 amps”? Understanding electrical power units is essential for ensuring the safety and efficiency of your home’s electrical system. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the basics of watts, amps, and volts, discuss how to calculate watts from 200 amps in both direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) circuits, and explain the National Electric Code (NEC) guidelines for electrical panels. Let’s embark on this electrifying journey!
Hello everyone, as a master electrician with over 25 years of experience under my belt I’ve been immersed in the world of electrical calculations, circuit designs, and power systems, honing my skills and deepening my knowledge every day. I’ve seen firsthand the rapid evolution of electrical technology and have been part of the journey, adapting and learning at every turn.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the interconnected relationship between watts, amps and volts to safely calculate power consumption.
- Calculate wattage from 200 Amps in both DC & AC circuits taking into account Power Factor & Phase numbers.
- Consult an electrician for panel upgrades to ensure safety, energy efficiency and greater electrical capacity.
Understanding Watts, Amps, and Volts
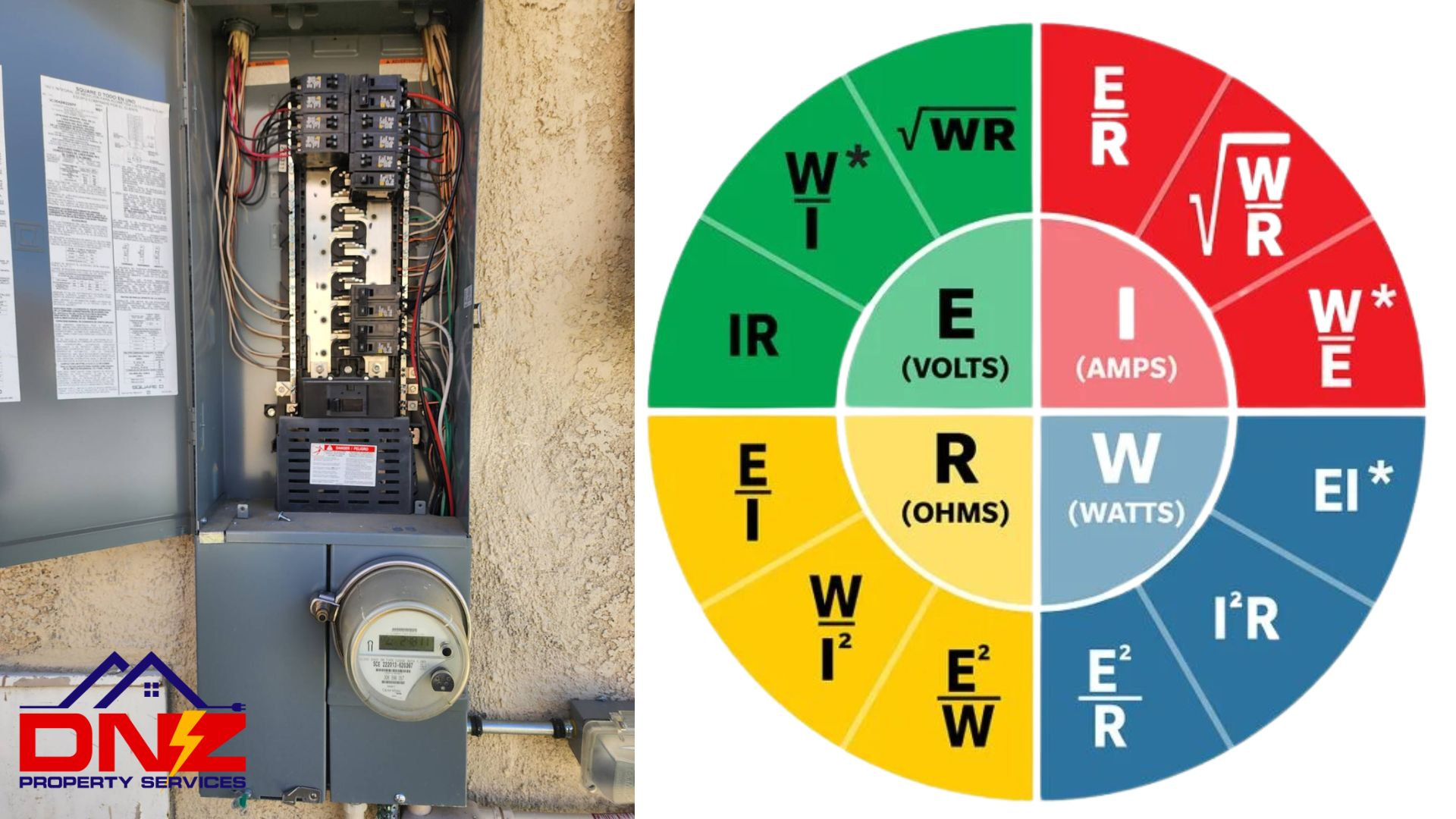
Before we delve into electrical power calculations, a solid understanding of electrical units is necessary. Watts, amps, and volts are the building blocks of an electrical system, and understanding their relationship is key to accurately calculating power consumption and ensuring the safety of your household. So, what are watts, amps, and volts, and how are they connected? Let’s find out.
Subsequent sections will delve into watts as the power unit, amps as the current flow measurement, and volts as the circuit’s potential difference. These interconnected units work together to help you accurately determine your home’s power requirements and maintain a safe electrical environment.
Watts: The Unit of Power
As a power unit, watts signify the rate at which energy is transferred or converted within an electrical system. In simple terms, a watt is equal to one joule per second, and it is used to measure the power consumption of electrical devices. Grasping the wattage of household appliances is important as it represents the power required for their proper functioning.
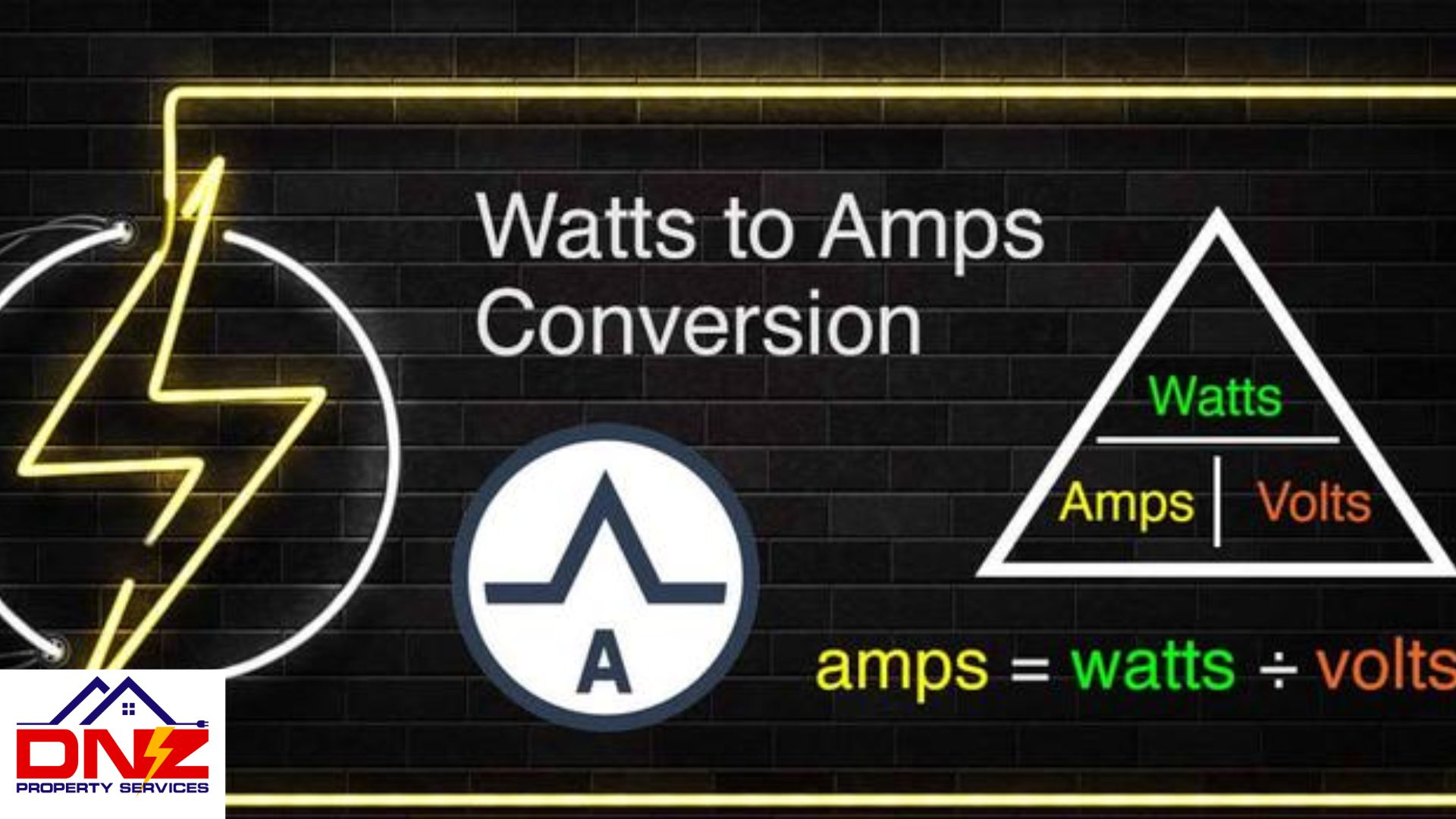
Watts calculation is a relatively simple process. The formula for determining watts is to multiply amps by line voltage. For example, if you have 200 amps and a line voltage of 120 volts, you would have 24,000 watts. Adhering to the National Electric Code (NEC) guidelines, such as minimum panel capacity requirements and the 80% rule, ensures that your electrical system operates safely and efficiently.
Amps: Measuring Current Flow
Short for amperes, amps quantify the rate at which electricity flows in a circuit. In other words, amps quantify the flow of electrons through a single-phase or multi-phase circuit. To measure current in a circuit and determine the number of amps, ammeters are utilized.
Power calculation using amps is also fairly uncomplicated. By multiplying the voltage by the current, you can determine how much power is being used in watts. This relationship between amps, volts, and watts forms the basis of understanding power consumption in a household and maintaining a safe and efficient electrical system.
Volts: The Potential Difference
In a circuit, volts denote the potential difference, equivalently referred to as electrical pressure. They measure the potential energy per unit charge in an electrical circuit, which is crucial for the operation of appliances like electric furnaces and water heaters. Understanding neutral voltage in such circuits can be essential for their safe and efficient functioning, and knowing the voltage type can further enhance this understanding.
Volts are measured using a voltmeter, a device that measures the potential difference between two points in an electrical circuit. To calculate watts, you can use the formula Watts = Amps x Volts. This interconnected relationship between volts, amps, and watts allows for accurate determination of your home’s power requirements and ensures the safe operation of electrical appliances.
Calculating Watts from 200 Amps
Armed with a firm understanding of watts, amps, and volts, we can now proceed to calculate watts from 200 amps in both direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) circuits. The fundamental equation for calculating watts from amps is Watts = Amps x Volts. However, the specific formula and examples will vary depending on the type of circuit (DC or AC).
Subsequent sections will demonstrate how to calculate watts from 200 amps in direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) circuits, taking into account the power factor and phase numbers.
Direct Current (DC) Conversion
Direct current (DC) is an electrical current that flows in a single direction, characterized by a unidirectional flow of electric charge. It is typically generated by sources such as batteries and solar panels.
To convert 200 amps to watts in a DC circuit, you can use the formula Watts = Amps x Volts. For example, if you need to convert amps to watts and the potential difference in a DC circuit is 10 volts, the calculation would be Watts = 200 Amps x 10 Volts = 2,000 Watts.
By using this formula, you can easily determine the power consumption of your DC electrical devices and ensure that your home’s electrical system operates safely and efficiently.
Alternating Current (AC) Conversion
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that reverses direction periodically and continuously varies its magnitude. To accurately convert 200 amps to watts in an AC circuit, you need to take into consideration the potential difference in volts (V), the power factor, and the number of phases.
When trying to determine how many watts are used in a specific electrical setup, consider this example: a 200 amp AC circuit with a potential difference of 120 volts and a power factor of 0.8 would yield a wattage of 19,200 watts, calculated as follows: 200 amps multiplied x 120 volts x 0.8, which represents the apparent power in this case.
By understanding the relationship between amps, volts, and watts in AC circuits, you can ensure that your home’s electrical system is safe and compliant with the National Electric Code (NEC) guidelines.
Household Wattage and 200 Amp Panels
Although a 200 amp panel is a prevalent choice for residential electrical systems, it’s vital to know its maximum wattage capacity and the risks of panel overloading. Overloading a 200 amp panel can lead to various issues, such as damaged appliances, increased risk of electrocution, and potential fire hazards.
This section will cover:
- The maximum wattage a 200 amp panel can withstand
- The potential risks and consequences of panel overloading
- The National Electric Code (NEC)guidelines for electrical panels, including minimum panel capacity requirements and the 80% rule.
Maximum Wattage for a 200 Amp Panel Box
A 200 amp panel can handle up to 48,000 watts, which is calculated by multiplying the amps by the volts. However, it is recommended to not exceed 80% capacity, which would be 32,000 watts, to avoid overloading the panel and causing potential safety hazards.
By adhering to the 80% rule and ensuring that your home’s electrical system does not exceed the maximum wattage capacity of a 200 amp panel, you can prevent overloading and maintain a safe and efficient electrical environment.
Overloading Risks and Consequences
Overloading a 200 amp panel can lead to several risks and consequences, such as damaged appliances, increased risk of electrocution, and damage to the entire panel. Some signs of an overloaded electrical panel include discolored or heated wall plates, a smell of burning wires emanating from the panel box, and hot components within the panel.
By understanding the potential risks and consequences of overloading a 200 amp panel, you can take the necessary precautions to avoid these issues and maintain a safe and efficient electrical environment in your home.
Adhering to the National Electric Code (NEC) Guidelines
The National Electric Code (NEC) is a comprehensive set of electrical rules and standards that must be adhered to for safe electrical design and installation. Compliance with the NEC guidelines is essential to ensuring the safety and conformity of your home’s electrical system.
In this section, we will explain the NEC guidelines for electrical panels, including minimum panel capacity requirements and the 80% rule. By adhering to these guidelines, you can guarantee the safety of your home’s electrical system and prevent potential hazards.
Minimum Panel Capacity Requirements
The NEC recommends a 100-amp minimum electric panel for houses. By adhering to this guideline, you can ensure that your home’s electrical system is adequately sized to handle the power demands of your appliances and other electrical devices.
It is also essential to follow the 80% rule, which stipulates that the aggregate wattage of all the appliances connected to a panel should not exceed 80% of the panel’s rated capacity. This rule helps guarantee that the panel does not become overloaded and provoke a fire or other safety hazard.
The 80% Rule
The NEC’s 80% rule suggests using only 80% of a panel’s capacity to avoid overloading and short circuits. For a 200 amp panel, this means that the maximum current draw should not exceed 160 amps.
By adhering to the 80% rule, you can ensure that your home’s electrical system operates safely and efficiently, minimizing the risk of overloading circuits and potential fire hazards. This rule is applicable to various applications, including EV charging and continuous loads such as motors and lighting.
Common High-Wattage Appliances
Certain high-wattage appliances that can contribute to overloading a 200 amp panel include:
- Electric heaters
- Air conditioners
- Electric stoves and ovens
- Electric water heaters
- Electric dryers
- Electric car chargers
Using these appliances simultaneously or for extended periods of time can put a strain on your electrical system. To ensure the safety and efficiency of your electrical system, consider spreading out the use of these appliances throughout the day or upgrading to a higher amp panel if necessary.
The following sections will highlight common high-wattage appliances that can burden a 200 amp panel’s capacity and potentially cause overloading:
- Air conditioners
- Heat pumps
- Electric ranges
- Stoves
- Washing machines
- Dryers
Air Conditioners and Heat Pumps
Air conditioners and heat pumps are high-wattage appliances designed to cool or heat a space. Air conditioners employ a refrigerant to cool the air, while heat pumps utilize a refrigerant for both cooling and heating the air. These appliances typically require between 500 to 4,000 watts of electricity for air conditioners and between 1,000 to 4,600 watts for heat pumps when running.
These high-wattage appliances can put a strain on a 200 amp panel, especially if the panel is not correctly sized to meet the wattage requirements of the air conditioner or heat pump. This can lead to an overload of the panel and potentially cause a fire.
Electric Ranges and Stoves
Electric ranges and stoves consume a significant amount of power, with wattage requirements ranging between 2,000 and 5,000 watts. These appliances can contribute to potential overloading of a 200 amp panel if the panel is not adequately sized to handle their power requirements.
It is essential to ensure that your home’s electrical system is properly sized and configured to accommodate the power needs of electric ranges and stoves, thereby preventing overloading and potential safety hazards.
Washing Machines and Dryers
Washing machines and dryers are other high-wattage appliances that can impact a 200 amp panel’s capacity. Washing machines typically require between 350 to 500 watts, while dryers need between 1,800 and 5,000 watts of electricity to operate.
Overloading a 200 amp panel with washing machines and dryers could potentially create a fire hazard, as well as cause damage to the wiring and appliances connected to the panel. It’s crucial to ensure that your home’s electrical system can accommodate the power demands of these appliances to maintain safety and efficiency.
Professional Assistance and Panel Upgrades
When it comes to upgrading your electrical system, understanding factors like “how many watts” your household appliances consume is crucial. At DNZ Property Services, we offer professional assistance that strictly adheres to the National Electric Code, ensuring your power consumption is both efficient and safe.
How Many Watts and Power Factor
Do you know how much power your electric furnace or electric range uses? By calculating watts, you can get a better understanding of your household wattage. This is especially important when you’re considering an electrical panel upgrade. Understanding power factor, a measurement of how effectively electrical power is being converted into useful work output, can also give you insights into your electrical system’s efficiency.
Line Voltage and Apparent Power
Line voltage and apparent power are critical elements to consider in any electrical panel upgrade. High line voltage can lead to increased power consumption and can be a fire hazard. Apparent power, which is a function of both real power and reactive power, can give you a comprehensive picture of how efficiently your electrical system operates.
Single Phase and Three Phase Systems
Whether your system is a single-phase or a three-phase system has a significant impact on your power factor and overall power efficiency. We can guide you through the technicalities of alternating current, voltage types, and more, helping you make the right decisions for your home.
Heat Pump, Electric Tank Water Heater, and More
Electrical panel upgrades aren’t just about managing existing power needs but also about planning for future appliances like heat pumps or electric tank water heaters. Knowing how much power these devices consume can help you decide whether you need a more substantial panel box.
Safety Measures
All our services come with state-of-the-art safety switches and measures to ensure that the power flowing through your circuit is secure. Voltage drop, burning wires, and electrical shocks are hazards that we actively mitigate during our upgrade services.
At DNZ Property Services, we specialize in full-scale electrical panel upgrades that comply with the guidelines laid down by the National Fire Protection Association. Contact us today to learn how we can help you modernize your electrical system, ensuring it’s up to current flow and amperage standards, optimized for your household’s specific needs.
By trusting us for your panel upgrades, you’re making a choice for a more secure and efficient electrical future.
Benefits of Panel Upgrades
Panel upgrades can enhance safety, optimize energy efficiency, and meet the electrical requirements of contemporary homes. Upgraded panels offer increased protection against power surges and other electrical issues, helping to mitigate the risk of electrical fires.
Additionally, panel upgrades can assist in decreasing energy expenditure by facilitating more proficient utilization of electricity. They can also provide an increased number of power outlets and a higher wattage capacity, enabling the simultaneous use of multiple electrical appliances.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding the relationship between watts, amps, and volts is crucial for maintaining a safe and efficient electrical system in your home. By adhering to the National Electric Code (NEC) guidelines and taking precautions when using high-wattage appliances, you can prevent overloading a 200 amp panel and ensure the safety of your household. Remember, when in doubt, consult a professional electrician for panel upgrades and to assess your home’s electrical needs. Stay safe and power on!
FAQ
Q: What size generator do I need for a 200 amp service?
A:
For a 200 Amp service, you should use a 15-20 kW GenSet to provide adequate power for your home. If you have air conditioning or other larger loads, opt for the larger size in the range. You may also need a line isolation panel installed by a professional.
Q: Is 200 amps enough for a house?
A:200-amp service is the current standard for new homes and can supply all standard electrical needs in a typical family home, but may not support a large electric heating system. In large homes, 300-amp or larger service capacity may be needed. Thus, 200 amps should be enough for most houses.
Q: How many watts is 12V 200a?
A:
12V 200Ah is equal to 2400 Watts (12 x 200).
Q.What is the largest breaker you can put in a 200 amp panel?
A:You can fit up to 100A circuit breakers in a 200 amp panel, making it the largest breaker you can install.
Q. 200 amps is how many watts?
A:200 amps is equal to 48,000 watts, given that you’re using 120 volts (which multiplies to 24,000 watts) or 240 volts (which multiplies to 48,000 watts). Depending on the voltage drop, wattage can range from 44,600 to 48,000 watts.